If you’re using the 5GHz band on your dual-band or a tri-band router and are still facing networking interference or facing slow internet speed issues, then you should consider switching to a different channel. However, the tough question is finding out the right wireless channel for your needs.
Since you’re here, you’re looking forward to finding the best Wi-Fi channel for the 5GHz band, well, there’s no one answer and the best might change depending on the network environment around you. So, does that mean living with slow internet? Well, no, you just need to find out the 5GHz channel that’s not crowded around you. But, how?
If you’re here just to find out the recommended channels then you can jump to that section of this post, but continue reading this if you’re interested in learning about different 5GHz channels and want to figure out the right channel based on your needs.
Table of Contents
Best 5GHz Channels & Bands in 2023
There are a total of 25 predefined 5GHz channels, they start from 36, 40, 44, 48 and go on until 149, 153, 157, 161 and 165. All of these wireless channels are not just used by routers, some of them are also used by the scientific industry and military stations for internal communication.
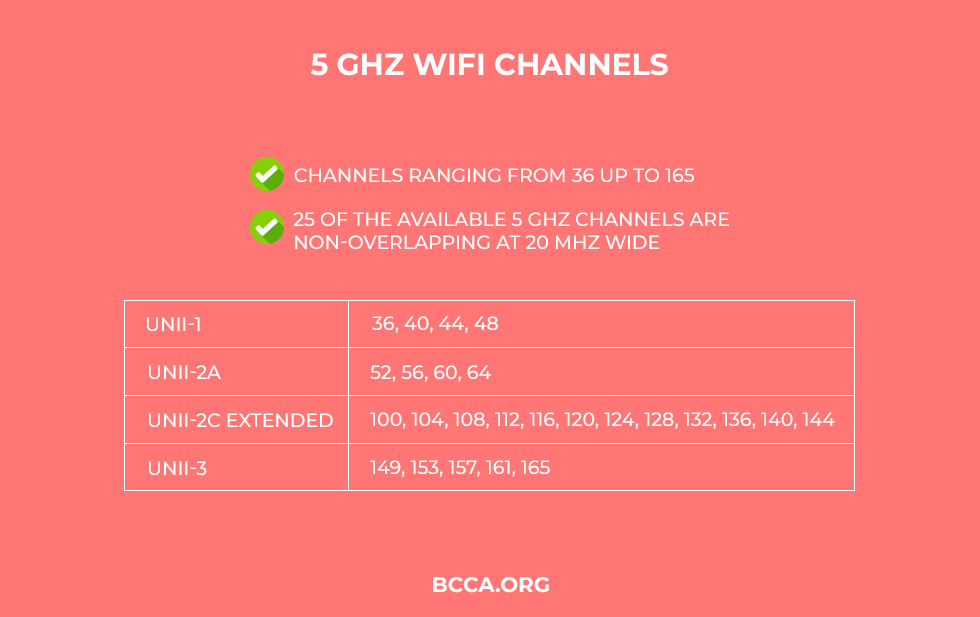
The channels are further segregated into different bands and each band serves a different purpose. These bands are known as UNII-1, UNII-2, UNII-3, and UNII-4. UNII stands for Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure.
Let’s see what the purpose of each of these bands is:
UNII-1 [For Home, Office, Business Area]
The first 4 wireless channels, that is, 36, 40, 44 and 48 are known as UNII-1 channels and they are generally used for domestic purposes.
They are the lowest available channels at 5GHz frequency band and the majority of your home devices run on them. This is also why there’s very high interference, but unless your router supports DFC/TPC, you’ll end up using this band.
UNII-2 [Routers with DFC and TPC]
This band consists of 4 channels as well – 52, 56, 60 and 64. They cannot be used by just about any device. Your router must have the DFS and TPC enabled to use the channels from this band.
DFS stands for Dynamic Frequency Selection and TOC stands for Transmit Power Control. DFS allows the router to automatically select the best channel without creating any overlap with the weather and military stations or any radars.
UNII-3 [For Industrial, Scientific, Medical Devices]
Also known as the UNII upper range, this band features channels 149, 153, 157, 161. This band is also known as the ISM range because it overlaps with the frequencies that are specifically designated for Industrial, Scientific, and Medical purposes.
This is because these are all higher channels, which means that they will have a wider bandwidth and better communication. Besides, DFS and TPC are needed to enable your device to use them.
UNII-4 [For Military Stations and Sensitive Communication]
This is the highest region and it is also known as DSRC or ITS. DSRC stands for Dedicated Short Range Communications and the 165 is the lowest channel which is a part of this band.
It is used for military stations and any type of sensitive communication. It is not recommended to use this channel, even if you have a device that supports it.
The Best 5GHz Channels For Wi-Fi at Home, Office, Business Place

The recommended 5GHz channels for home usage are UNII-1 (36 40 44 and 48) and you can go farther up and select the higher ones if your router has DFS and TPC.
Note: Higher channels are recommended because you will find less interference.
One more thing that you should keep in mind is that the regular smart devices as well as the smart home appliances also use the UNII-1 channel for communication.
Therefore, you might experience some interference between your router and these devices. The only solution for this is to make sure that your router is placed far from any smart devices like smart home appliances and smart bulbs.
Another issue worth keeping in mind is congestion. Since it is clear that the UNII-1 band is highly suitable for Wi-Fi, almost all the devices at your home will be connected to the internet via this band. This may lead to congestion because of which there might be a drop-in the Wi-Fi performance.
To handle this, you can use various types of Wi-Fi analyzer apps on the internet. These apps check for channel congestion in your vicinity and the best channel for you. This way you can get the best performance out of your wireless connection.
These apps can also show you how many devices are on a particular channel and they’ll also give you a rating for every one of them, so you can pick the best one for you. Which brings me to my next point, how to find which one is suitable for you?
How to Find the Best Wi-Fi Channel at your Place?
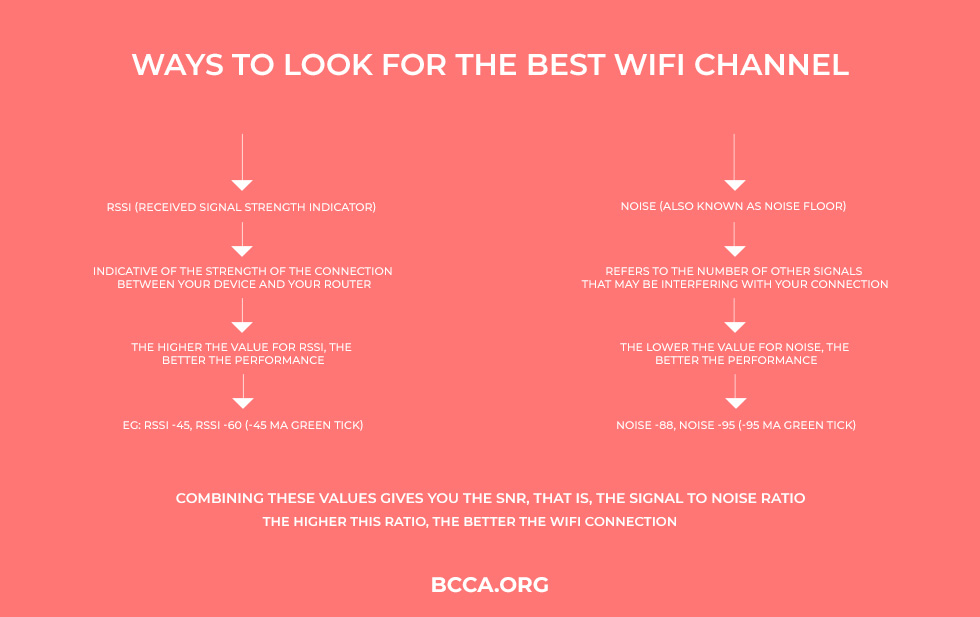
When you are looking at the Wi-Fi data for finding the best Wi-Fi Channel there are two things that you need to consider – RSSI and Noise.
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) is indicative of the strength of the connection between your device and your router.
Noise (Noise Floor) refers to the summation of all the unwanted signals and sources of noise within the range of your connection.
Note: Both of these values will always be negative.
Higher Value for RSSI and Lower Noise = Best Channel
For RSSI, you need to remember that you have to check the highest number, that is, the higher the value for RSSI, the better the performance.
On the other hand, the Noise value should have a low number. But for both of these numbers, you have to remember that the value is negative.
So, for instance, if Channel A has RSSI -45 and Channel B has RSSI -60, Channel A is better, because this number is higher. You can remember the thumb rule that the RSSI value should be closer to zero.
But for Noise, the reverse is true. If Channel A has Noise -95 and Channel B has -88, then A is better. Think of it like the channel having a Noise value furthest from zero is better.
Combining these values gives you the SNR, that is, the Signal to Noise Ratio. The higher this ratio, the better the Wi-Fi connection is. You can calculate this value by subtracting the value of Noise from RSSI.
For instance, if a channel has RSSI of -39 and Noise is -86, then SNR is (-39) – (-86) = -39 +86 = 47.
How to Find RSSI and Noise on Mac, Windows, Android?
1. Mac
Follow the steps below to find the best Wi-Fi channel on Mac:
- Hold the Option or Alt Key, and at the same time, click on the Wi-Fi connection icon at the top-right corner of your screen.
- In the drop-down menu, select “Open Wireless Diagnostics”
- A new window will open, called “Wireless Diagnostics” (Do not click or do anything in this window.)
- Go to the title bar and click on “Window” and Select “Scan” from the drop-down menu.
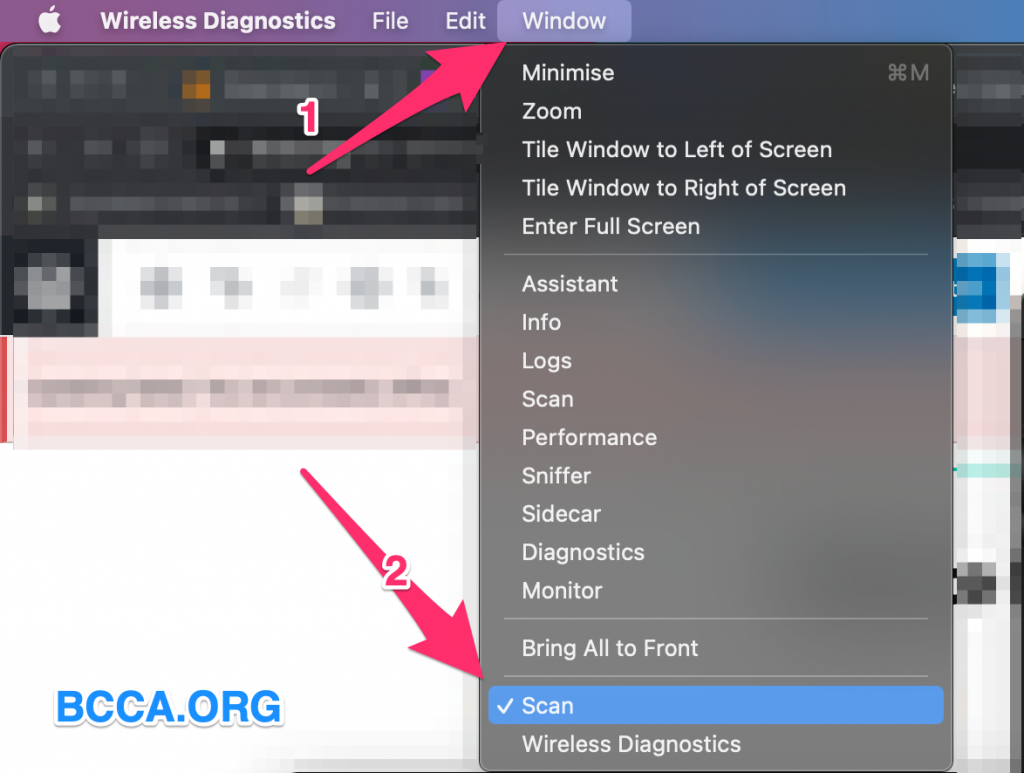
- Now you will see a window that has an overview of all the Wireless Access Points within the range of your router.
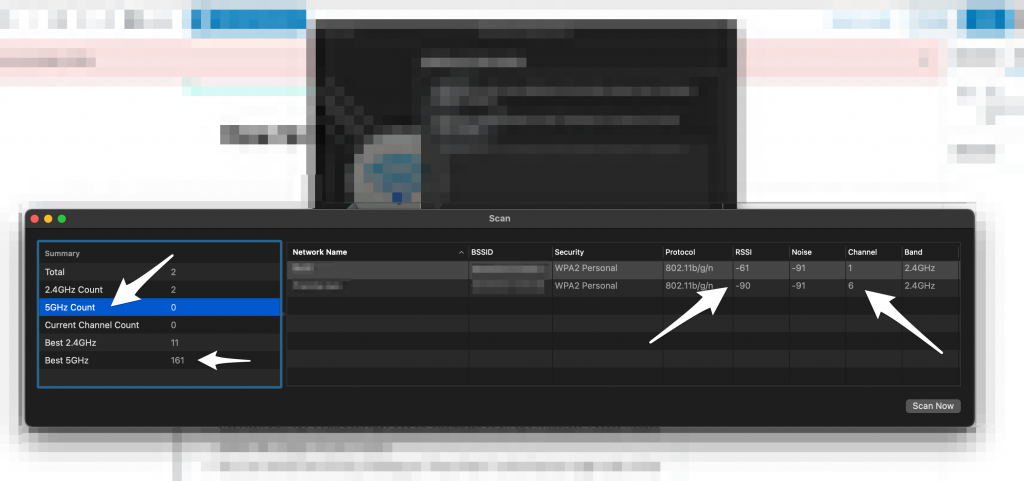
- You can refresh the list by clicking on “Scan Now” at the bottom right side of the window.
This window shows a complete overview of the analysis of the Wi-Fi channels in the area as well as the best Wi-Fi channel in the area of your router. Even though the window will have a suggestion for the best channel, it is better to make some calculations and find out on your own which channel is the best.
Low SNR (RSSI minus Noise) = Best Channel
By now, you know that the best channel is one that has the best SNR value. For instance, if channel “A” has RSSI of -49 and Noise is -95, while Channel B has RSSI -46 and Noise is -99, Channel B is the best channel as it has an SNR of 53, whereas the Channel A has SNR of 46.
2. Windows
Unlike Mac, you will have to use an app or software to find out the best Wi-Fi channel in your area on Windows. Here are some suggested apps:
- NetSpot – compatibility with Windows 7,8 and 10
- Wi-Fi Analyzer – compatibility with Windows 7,8 and 10
- Wi-Fi Commander – compatibility with Windows 10
- Acrylic Wi-Fi – official app available on the Microsoft Store
All these apps are pretty powerful and can help you with scanning and finding the best channels in your area. Since Wi-Fi Analyzer is available on the official Windows Store, let’s take it as an example and see how you can find the best channel using this app.
- After you have downloaded and installed the app from Microsoft Store, open it.
- You will see the current channel of each of the connections on the dashboard, written under the name of the network. On the right side of the dashboard, there are some extra filters, but you do not need to change the default settings.
- Now click on the Analyser button on the dashboard. You will see a graph with many visuals, including information of which network is performing in the best way. Below the graph, you will see recommendations on the best channel.
But if the graph seems too complicated, you can also simply check the bottom left side of the dashboard where you will see the recommended channel. However, you do not need to rely on the readings. You can check for yourself.
As I have established before, the closer RSSI of a channel is to 0, the higher performing the channel is. So, if channel A has dBm -50 and channel B has dBm -60, Channel A is better because -50 is closer to zero than -60.
dBm refers to RSSI signal strength and basically, the closer it is to 0, the better.
3. Android
The best tool for finding the best Wi-Fi channel on Android is Wi-Fi analyser, the same one I mentioned above. You can download it from the Play Store. After that, follow these steps:
- Launch the app and open and dashboard
- Check the dBm of the available channels. You can also use the graph function to compare all the networks available visually.
- The channel with the RSSI closest to zero is the best.
What is 5GHz Frequency?
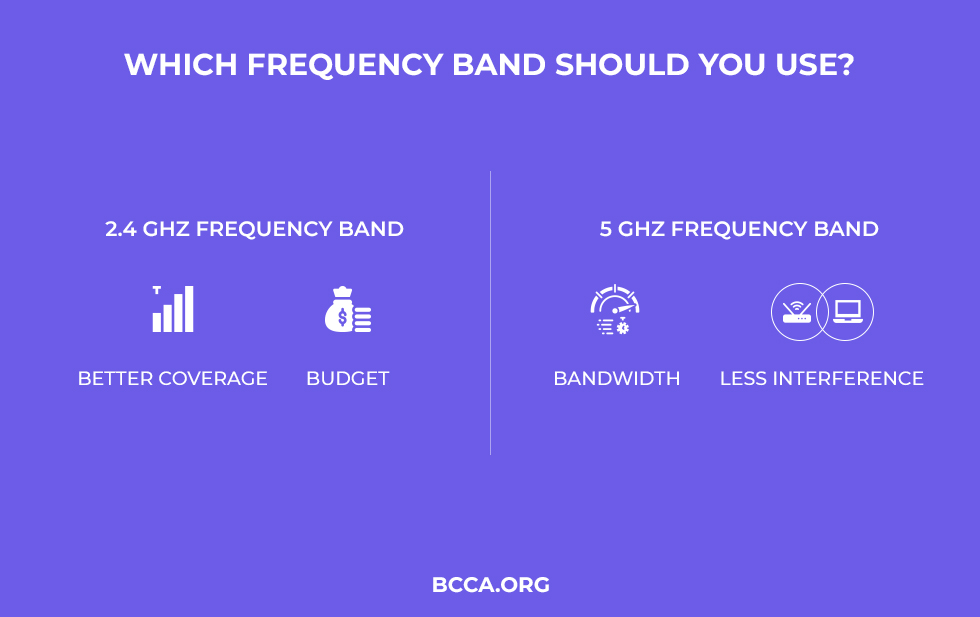
The two most commonly used Wi-Fi frequency bands are 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
But before I explain what exactly Wi-Fi frequency bands are, you need to understand how routers work. Your router is basically a network device that is used to transmit data to your devices through radio waves.
The router transmits radio waves in all directions and your devices connected to the Wi-Fi or the router receive this data. This is the simplest explanation of how a router works. The next concept that comes into play is bands and channels.
Both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies have their own advantages and disadvantages, but the most basic thing is that the 2.4GHz frequency comes with lower bandwidth and a wider range. On the other hand, 5GHz frequency has higher bandwidth but a shorter range, which means that it has better performance than 2.4GHz frequency but the coverage area is smaller.
In other words, a 5GHz wireless connection is good for getting faster internet speed at a small distance, whereas the 2.4GHz wireless connection can cover farther distances, but it might do that at a lower speed. This also means that a 5GHz connection is not as good as the 2.4GHz connection for penetrating walls and objects.
Now coming to the idea of channels, they are basically the width of the band at which a router releases the signals in the open space. The higher frequency a channel has, the wider is its bandwidth. You will also notice that an increase in channel frequency also leads to a massive improvement in the performance of the Wi-Fi network.
The reason the 5GHz channel is expressed as a whole number but the other one has the dot 4 is because the 5GHz channel covers a wide range of channels, from 5.15GHz to 5.85GHz. For the sake of simplicity, it has been shortened to 5GHz. On the other hand, the 2.4GHz channel has its entire range within the band of the same frequency.
Also, the channel is commonly designated as 5G and it became very commonly used after the 802.11a network connection version debuted. The 5GHz band is also very commonly used in the later versions of Wi-Fi, such as 11n, 11ac and 11ax.
Frequently Asked Questions
Every Wi-Fi channel is allotted a segment of 20 MHz within its frequency band. The width of the channel actually dictates how much data can pass through it and at what speed the data will pass.
Wider channels always have more data allowance and at faster speeds, given that they are not impeded by interference from other devices. Moreover, there are certain frequency bands that are more commonly affected by interference, and on the basis of this, there are certain Wi-Fi channel width settings for routers as well as access points are recommended.
So, yes, the channel width is quite an important factor.
The three differences between these two frequencies are range or coverage, bandwidth or speed, and interference.
In short, yes, higher 5GHz channels will provide wider bandwidth and better communication. But since several higher 5GHz channels are limited to military and scientific usage, you are limited to the UNII-1 channels. Of these, the best channels are the higher ones, as they have wider bandwidth.
Conclusion
A faster Wi-Fi connection is the modern-day equivalent of Oxygen. You need it to stay alive. But to reach the full potential of your wireless connection, you need to start paying attention to the data.
The Wi-Fi diagnostics are life-changing and simply being able to read a few numbers and understanding how they work can massively boost your internet speed. This is especially helpful if you live in a congested area or share your Wi-Fi with other people.
So, with this information, you are equipped to never suffer from a slow connection ever again. Connect to a faster Wi-Fi channel and live your best life. Happy surfing!
Chris loves technology, specifically smart home technology! With both hands-on and executive leadership experience in his corporate career, Chris stays abreast of emerging technology and solutions and immerses himself in BCCA when not in the office.