You might have come across the term ‘frequency band’ while reading my guide to purchasing a wireless router. You also must have noticed that are there are two frequency bands; 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
They are different radio wavelengths used by wireless routers to transmit data packets. The primary difference between both the frequency bands is in terms of their coverage and speed.
According to physics laws, higher the frequency, lower the wavelength. It basically means, higher the GHz, lower is the coverage.
Therefore, even though the frequency of 5GHz is higher than the 2.4GHz band, its coverage is lower and it cannot penetrate walls like the 2.4GHz frequency band can. That being said, if you want a faster wireless connection and are located near the router, you should connect to 5GHz frequency. However, if you are away and have walls/objects in between, then consider using the 2.4GHz frequency.
The difference between both frequency bands isn’t limited to just coverage and bandwidth. There’s a lot more about them than what meets the eye. In case you’re interested to learn the in-depth difference between both, then read on!
Table of Contents
What is a Frequency Band?
A frequency band is defined as a frequency interval that is delimited by a minimum and maximum frequency.
Basically, the term refers to radio frequency bands, but it can also refer to some other spectrum. The frequency band provides a satisfactory performance with minimum distortions only over a certain range known as the ‘frequency range.’
They can be further broken down into Wi-Fi channels which are a medium through which wireless networks send and receive data. In the computer, local area networks, radio frequencies of the range 2.4GHz, and 5GHz are used.
2.4GHz vs 5GHz Quick Comparison
| SPECIFICATION | 2.4GHz FREQUENCY BAND | 5GHz FREQUENCY BAND |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | It is the most widely accessed frequency band which is available in Wi-Fi standards 802.11b/g/n. It has a lower frequency limit of 2400 MHz and an upper-frequency limit of 2500 MHz. | It covers a bandwidth of 150 MHz from 5.725 MHz to 5.875 MHz. The range of the frequency band can be widened up to 750 MHz using an additional range of Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure (UNII). |
| Range | The 2.4 GHz frequency band has a lower frequency and can hence travel a larger distance due to its higher wavelength. Moreover, due to its higher wavelength, it has a better penetration power. It has a maximum range of up to 410 ft. from the router. | The 5 GHz frequency band has a higher frequency and hence according to the basic laws of physics, it has a lower wavelength. Therefore, it cannot travel farther than 10-15 ft. from the router. Moreover, it cannot penetrate solid objects well and is hence, not recommended for large houses with lots of furniture. |
| Overlapping Channels | A Wi-Fi frequency band is sub-divided into numerous Wi-Fi channels. The 2.4 GHz frequency band is divided into 14 Wi-Fi channels. Out of these only three channels are non-overlapping. Non-overlapping channels are the ones where there is the least data traffic. In the 2.0 GHz frequency band the Wi-Fi channels 1,6, and 11 are the non-overlapping and the rest are overlapping channels that experience co-channel and adjacent channel interference. | As you know, a Wi-Fi frequency band is broken down into several Wi-Fi channels which are responsible for sending and receiving data packets from the Wi-Fi stations. In a 5 GHz frequency band, there are more number of non-overlapping channels. These non-overlapping channels are responsible for providing the 5 GHz frequency band with greater speed due to minimum co-channel and adjacent channel interference. |
| Operating Frequency | The 2.4 GHz frequency band has 14 channels. These channels are of 20 MHz each and operate in the frequency range of 2,400 and 2,483.5 MHz. | In the 5 GHz frequency band, channels 20-26 are safe to be used by the public. Here each channel is 50 MHz wide and it operates in the frequency range of 4940 MHz to 4990 MHz. In fact, out of these channels, channel numbers 22 and 26 are most frequently used. |
| Uses | The 2.4 GHz frequency band is suitable for you if you have a huge home with lots of furniture and require your Wi-Fi to reach the maximum corners of the house. It has better penetration power and can travel a longer distance as compared to the 5 GHz frequency band. | The 5 GHz frequency band is most suited for you if you’re looking for a wireless connection to satisfy your business and gaming requirements. It doesn’t penetrate the solid objects and has a lower range as compared to the 2.4 GHz one. But, it has better speed and less co-channel and adjacent channel interference. |
| Distance | As you already know, this has more penetration power and hence it can travel longer distances. The Wi-Fi Alliance claims that the 2.4 GHz frequency band can travel a distance of up to 410 ft. from the router. | The 5GHz frequency band may have greater speed, but it falls short in terms of traveling the distance. It provides a strong signal only up to a distance of 15 ft. from the router. |
| Speed | The 2.4 GHz frequency band has only three non-overlapping Wi-Fi channels. Moreover, as it is commonly used by several household devices, it encounters more co-channel and adjacent channel interference. Due to all these hindrances, it can only provide a practical maximum speed of 100 Mbps. | The 5 GHz frequency band has a higher number of non-overlapping channels available. Moreover, as its a fairly new Wi-Fi addition, fewer devices are compatible with it leading to lesser co-channel and adjacent channel interference. Therefore, this provides you a faster Wi-Fi connection as compared to the 2.4 GHz frequency band. |
| Device Compatibility | The 2.4 GHz frequency band is compatible with almost all your household devices be it microwave, ovens, refrigerators, laptops, computers, etc. It is also compatible with several outdated devices. | The 5 GHz frequency band came in later than the 2.4 GHz frequency band and hence it is compatible with only newer devices. You’ll have to check with the manufacturer of your personal devices to know whether they are compatible with the 5 GHz frequency band or not. |
| Wi-Fi Channel Widths | The 2.4 GHz frequency band is an outdated Wi-Fi version and that’s why it has 14 Wi-Fi channels which are only 20 MHz in size. You can club these channels together for a higher channel bandwidth. | The 5 GHz frequency band is a newer Wi-Fi version and hence it provides you the option to choose from 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, and even 160 MHz wide channels. |
| UNII and ISM Bands | The ISM bands stand for industry, scientific, and medical frequency bands which are reserved for other purposes rather than communication. It has 14 ISM Wi-Fi channels out of which except the last channel, every channel is 5 MHz apart. | It is divided as follows: UNII-1: Channels: 36, 40, 44, 48 UNII-2a: Channels: 52, 56, 60, 64 UNII-2c Extended: Channels: 100, 104, 108, 112, 116, 120, 124, 128, 132, 136, 140, 144 UNII-3: Channels: 149, 153, 157, 161, 165 |
| Wi-Fi Channel Combination | It allows the combination of Wi-Fi channels up to 20 MHz only. | It allows multiple permutations and combinations of Wi-Fi channels up to a maximum of 160 MHz. |
| Ethernet Connection | It provides you a more stable ethernet connection as compared to the 5 GHz frequency band. | It may drop a few times while it’s connected to your PC through an ethernet cable. Therefore, the 2.4 GHz frequency band wins in terms of stability. |
| Applications | The 2.4 GHz frequency band is used for everyday tasks such as emailing, web surfing, watching videos, etc. | The 5 GHz frequency band provides you better throughput and is usually recommended for media streaming, pictures, business purposes, and gaming. |
The 2.4 GHz Frequency Band
2.4 GHz is a data connection that works on the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Single-band Wi-Fi routers used to employ it for data transmission. Nowadays, dual-band and tri-band routers use both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.

The 2.4 GHz frequency band is compatible with all household devices such as computers, laptops, smartphones, ovens, television, etc. That’s why this frequency band can get congested and lead to Wi-Fi dead zones.
However, the 2.4 GHz band on Wireless routers have some major benefits such as better coverage and the ability to penetrate solid objects.
For instance, if you live in a big house with lots of rooms and solid objects in the way, then undoubtedly the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi is the best option for you. Moreover, it is compatible with all the older devices.
How Fast is the 2.4GHz Frequency Band?
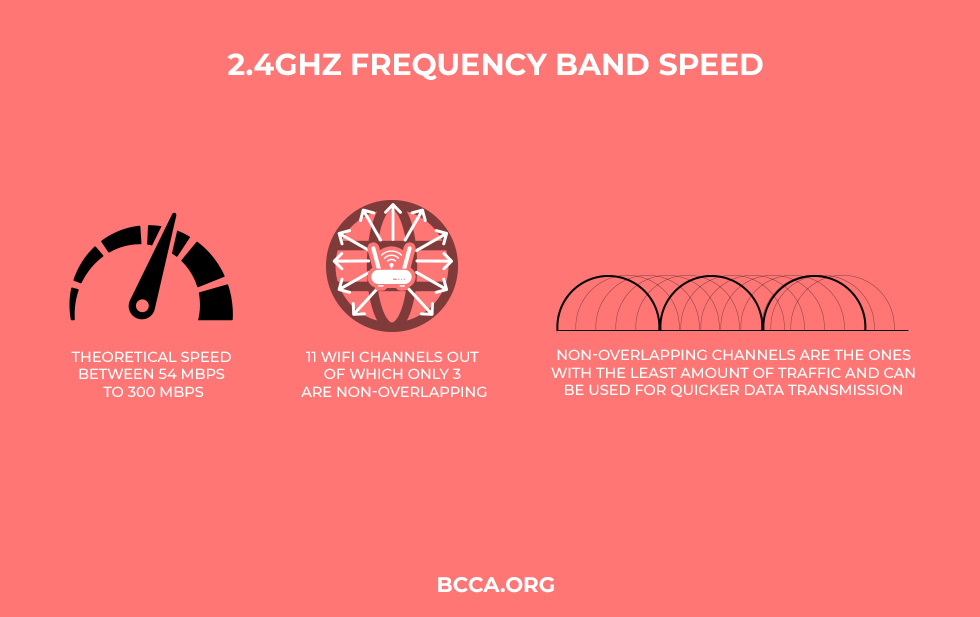
The 2.4 GHz frequency band provides you a theoretical speed between 54 Mbps to 300 Mbps. It has 11 Wi-Fi channels out of which only 3 are non-overlapping. Non-overlapping channels are the ones with the least amount of traffic and can be used for quicker data transmission.
The problem with this frequency band is that cordless phones, microwaves, televisions, etc. send out radio waves of the same frequency. That’s why they can interfere with your wireless data transmission. This is known as co-channel interference.
For instance, think of the 2.4 GHz frequency band as a highway. If lots of cars use the same highway then it can lead to never-ending traffic. However, if the same highway has lanes that lead to the same destination, then indubitably you’ll travel seamlessly.
The same happens with your data packets of information. Due to a large amount of co-channel interference, the 2.4 GHz frequency band offers a slower speed.
What is the Range of 2.4 GHz Band?
Like mentioned above, basic physics tells you that the higher the frequency, the lower the wavelength or bandwidth will be. Since the 2.4 GHz frequency band has a lower frequency, its range is much better than the 5 GHz frequency bands. Also, it can penetrate solid objects better than other frequency bands.

This means that if you have a large house with lots of rooms and furniture, then the 2.4 GHz frequency band will be your best friend in terms of wireless connection. It has a range capacity of 63 ft. to 430 ft. However, due to its large range, it has a slower speed.
Think of it this way. Whenever you roll out some dough with a rolling pin, it gets thinner as it expands. The same happens to your frequency band. As the range for the 2.4 GHz frequency band increases, its density decreases.
2.4 GHz Channels

The 2.4 GHz band is broken down into 11 Wi-Fi channels, out of which only 3 are non-overlapping. These are channels 1, 6, and 11. These non-overlapping channels do not interfere with other channels. Channels 2-5 can interfere with channels 1 and 6. And channels 7-10 can interfere with channels 6 and 11.
In layman terms, when your Wi-Fi station has some data packets to transmit, it must wait for the Wi-Fi channel to be clear. This means that only a single device can transmit data packets at a given point of time.
However, when you use non-overlapping channels, each Wi-Fi station transmits data packets irrespective of the other channels. This type of interference is known as Adjacent Channel Interference and it can ultimately lead to degradation in the performance of your Wi-Fi.
Co-channel interference occurs when two or more access points in the same area try to transmit data packets using the same channel. This is caused due to a lot of your household devices trying to gain access to the same wireless transmission channel. Therefore, it is recommended that you use only the non-overlapping Wi-Fi channels of 20 MHz each.
2.4 GHz Routers
The single-band routers use the 2.4 GHz frequency band whereas dual-band and tri-band routers use both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. Generally speaking, single-band routers have a slower wireless data transmission rate and it also covers a smaller area.
For your everyday tasks of net browsing, sending emails, and watching movies, a single-band router is enough. However, for business tasks and gaming, you require better speed which is provided by dual-band and tri-band Wi-Fi routers.
How do I know if I have 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi?
To check if you have 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, go to the settings section of your smartphone, and select Wi-Fi (Wireless Network). If you see only one Wi-Fi network, that means you’re connected to a single-band router that operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
However, if you see two Wi-Fi networks, that means you’re using a dual-band router. A 2.4 GHz frequency band may be labeled as 24G, 2.4, or 24. A 5 GHz frequency band may be labeled as 5G or 5.
If you’re unable to see any such network associated with the name 2.4 or 5, then it means that your Internet Service Provider has changed the name of one of your frequency bands.
To find out further information, you’ll need to log in to your Wi-Fi router. Once you’ve logged in to your wireless network, then you’ll be able to see the name of your Wi-Fi frequency bands.
- Covers a larger area
- Better at penetrating solid objects
- The maximum theoretical connection speed of 300 Mbps
- Maximum signal range from the router of 410 ft.
- Even outdated devices are compatible with this frequency
- Low data transmission rate
- More prone to co-channel and adjacent channel interference
- More devices compatible hence more interference experienced
- Only three non-overlapping channels
The 5 GHz Frequency Band
A 5 GHz wireless router employs the 5 GHz frequency band for the data transmission. Although the 802.11b wireless standard operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, the later Wi-Fi standards operate on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
The 5GHz frequency band came into operation to minimize the digital noise that was caused due to multiple device compatibility with the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
Some Wi-Fi standards even let you pick between the 2 frequency bands. However, even with all its advantages, a larger portion of users continue to use the 2.4 GHz frequency band due to better coverage.
If you’re getting a modern router, then you’ll get to use both 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz which is really helpful. Thereby allowing you to switch between bands when needed.
How Fast is the 5 GHz Frequency Band?
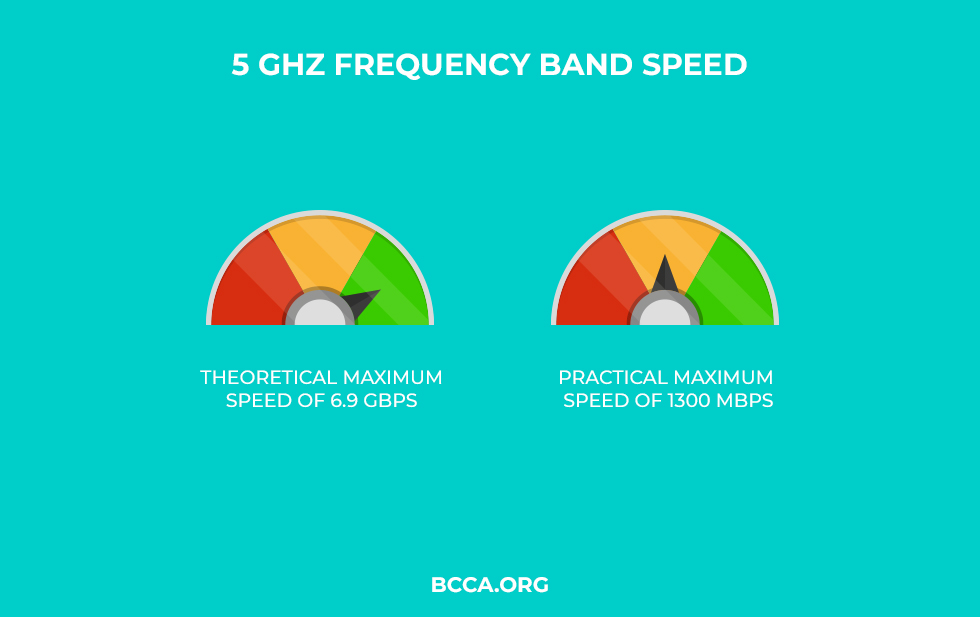
The 5 GHz frequency band can provide you a theoretical maximum speed of 6.9 Gbps and a maximum practical speed of 1300 Mbps.
Just like the 2.4 GHz frequency band, this one also has a set of overlapping and non-overlapping channels. However, unlike it, the 5 GHz frequency band have more number of non-overlapping Wi-Fi channels. Moreover, very few devices are compatible with this frequency band.
This leads to lesser co-channel and adjacent channel interference. Therefore, the 5 GHz frequency band is able to provide a faster data connection than the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
What’s the Range of 5 GHz?
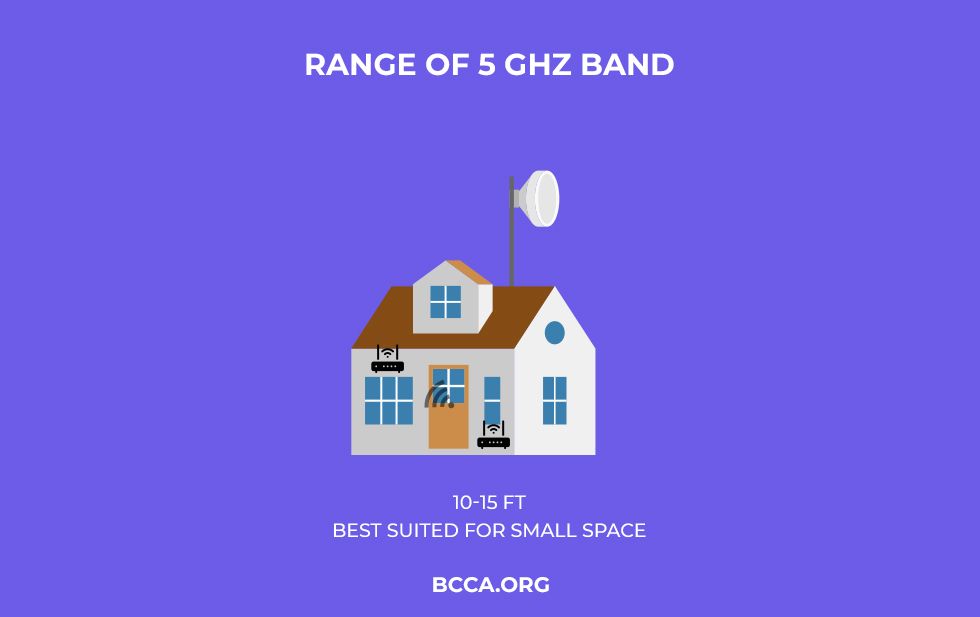
The 5 GHz band provides you a maximum practical range of 10-15 ft.
Just like I said earlier, higher frequency bands have lower bandwidth or range according to some basic physics laws. That’s why the 2.4 GHz frequency band provides you a better range. That’s really low as compared to the range of 2.4 GHz band. However, it does have its benefits of better uploading and downloading speed.
The 5 GHz Wi-Fi Channels
In a 5 GHz router, every channel has its own 20 MHz non-overlapping bandwidth. Also, 802.11n wireless standard allows you to use 40 MHz wide channels, 802.11ac allows you to use 80 MHz wide channels and the latest Wi-Fi standard 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) allows you to operate 160 MHz wide channels.
All of this is possible due to a combination of various 20 MHz channels. Wider channels increase the throughput of your wireless connection. Try to understand it this way. Wider highway roads will be able to handle much more traffic easily and people will be able to reach their destination faster.
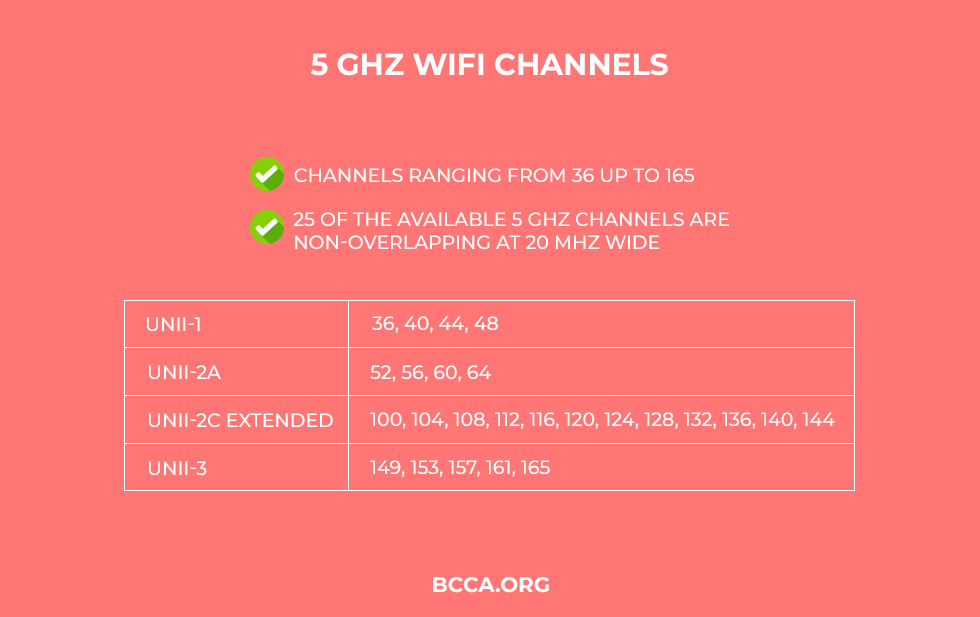
The same goes for wider Wi-Fi channels which allow faster data transmission. The 5 GHz frequency band has the following Wi-Fi channels:
| 5 GHz Frequency Band Units | 5 GHz Channels |
| UNII-1 | 36, 40, 44, 48 |
| UNII-2a | 52, 56, 60, 64 |
| UNII-2c Extended | 100, 104, 108, 112, 116, 120, 124, 128, 132, 136, 140, 144 |
| UNII-3 | 149, 153, 157, 161, 165 |
5 GHz Routers

Most modern-day Wi-Fi routers employ both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. Let’s talk about each one of them:
Dual-Band Routers
The 5 GHz frequency band was introduced into the wireless world. The fewer number of devices are compatible with it which is why it provides you with a better user experience.
Dual-band is a dedicated Wi-Fi network for business and gaming purposes.
Tri-Band Router
Tri-band routers employ one 2.4 GHz and two 5 GHz frequency bands.
It can support more devices and provides three times greater bandwidth.
It also experiences less interference than other routers.
How Do I Know If I Have 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
To find out whether or not you’re connected to the 5 GHz frequency band or not, go to the settings section of your smartphone and open the wireless connection tab.
If you only see one wireless network, then it means that your smartphone is connected to the 2.4 GHz frequency band of the router. However, if you see two wireless networks, one of them will be the 5 GHz frequency band.
Now notice if there’s a number written next to the name of your wireless network. In the case of a 2.4 GHz frequency band, the number 2.4 or 24G will be written next to the name of your wireless network. And in the case of a 5 GHz frequency band, the number 5 or 5G will be mentioned.
If you don’t notice any number beside the name of your wireless connection, then chances are that your network provider has changed the name of the network frequency band.
So, to find out which frequency band you’re connected to, you’ll have to log in to your wireless router and go to the wireless settings section. There you’ll be able to see the name of the Wi-Fi frequency band your device is connected to.
5 GHz Frequency Band: The Pros & Cons
- Provides a practical maximum speed of 1300 Mbps.
- Experiences less co-channel and adjacent channel interference.
- It provides more non-overlapping Wi-Fi channels.
- Includes more dynamic features such as beamforming, frequency selection, and transmitting power control.
- Does not penetrate solid objects efficiently.
- Travels shorter distances.
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Simultaneously
As you’re already aware of, dual-band routers are the ones that use both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, frequency band. It can transmit data packets by using both the frequencies separately or using them simultaneously. It totally depends on your personal choice. Let’s have a look at them both, shall we?
Selectable Dual-Band Router
The selectable dual-band router allows you to pick between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. You can opt for either of them according to your requirements. Remember, if you opt for the 5 GHz frequency band, make sure that your devices and adaptor are compatible with it. If they’re not, then don’t change the frequency preference of your router.
Simultaneous Dual-Band Router
As the name suggests, the simultaneous dual-band router operates on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands simultaneously. This allows you better throughout as you have two dedicated frequency bands at your service. It allows you more flexibility while working and also greater bandwidth.
2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz: Which Frequency Band Should You Use?
Both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands have different uses. Choosing the best one according to your needs is a must if you want a better overall user experience. Let’s have a look at the factors to be noted while choosing between both the bands:
Coverage
If coverage is the factor that seals the deal for you, then you have to go for the 2.4 GHz frequency band. It covers a larger area and reaches every nook and cranny of your house. However, you might have to compromise on the speed of this. In the case of the 5 GHz frequency band, you’ll have to broaden the number of access points.
Speed
If speed is the determining factor for you, then you need to pick the 5 GHz, frequency band. It provides better throughput due to less co-channel and adjacent channel interference. Therefore, its best suited for business and gaming purposes.
Bandwidth
If your priority is better Wi-Fi performance, then you’ve got to go for the 5 GHz frequency band. It provides excellent performance targeting business travelers with faster Wi-Fi connection and throughout.
Interference
If you’re experiencing several Wi-Fi dead zones then its because your data is being transmitted through several overlapping Wi-Fi channels. This is a common problem encountered while using the 2.4 GHz frequency band. This is because more household devices are compatible with the 2.4 GHz frequency band leading to more co-channel and adjacent channel interference.
Budget
The price of 2.4 GHz frequency access points is lower than the 5 GHz frequency access points. Therefore, if you’re in a pinch, its best to buy the 2.4 GHz, frequency band.
How to Find Out Which Frequency Band You are Connected To?
In case you’re using a smartphone or a laptop or your PC, go to the settings section of your device and select the wireless network option. There you’ll have to notice whether only one wireless network is available or more. If only one wireless network is available, that means that your device is connected to the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
However, if more than one wireless network is visible in the settings section then try to notice if any number is visible besides the name of your network.
If you can see the number 2.4 or 24G then it means you’re connected to the 2.4 GHz frequency band. If you can see the number 5 or 5G then it means you’re connected to the 5 GHz frequency band.
In case you can’t see any numbers next to the name of your wireless network, then it means that your Internet Service Provider has changed the name of the frequency band. You’ll have to log in to your device and check for the Wi-Fi frequency band type.
Conclusion
The world is so technology-driven that it’s important for you to be familiar with the basics of the wireless connection you are using.
A wireless connection supports everyday tasks and provides you with a medium to entertain yourself throughout the day. Be it just casual web surfing or business and gaming requirements, your wireless device must have the ability to help you fulfill your tasks with ease.
After reading this, not only would you have in-depth knowledge about both the frequency bands (2.4GHz and 5GHz) but you’ll also know their pros, cons, suitability, which will help you decide the best band for your usage.
Chris loves technology, specifically smart home technology! With both hands-on and executive leadership experience in his corporate career, Chris stays abreast of emerging technology and solutions and immerses himself in BCCA when not in the office.
