A bad router is a nightmare for everyone. After all, everyone’s so addicted to using the Internet to carry out our daily tasks, that living without it can simply be impossible. From gaming, surfing, streaming, to important business tasks; everything gets impacted equally when your networking equipment has issues.
It doesn’t matter whether you buy your own router or rent it from your Internet Service Provider (ISP), the device can encounter several problems nevertheless. The most common problems users face when their Wi-Fi stops working are slow upload and download speeds, poor signal strength, continuous disconnects, dead zones, etc.
There are indicators that can tell you whether your Wi-Fi is completely broken or is in the process of breaking. If it’s the latter, then you can fix your Wi-Fi at home with some little tricks. And if not, then maybe it’s time to replace your bad old router with a new one. I’m sure that there are a million questions plaguing your mind right now.
I’ll make sure that this article answers each and every one of them. So, let’s dive further into the details about how to tell if your router is bad and what to do about it.
Table of Contents
- How to Identify a Bad Router? [2023 Edition]
- How to Avoid Buying a Bad Router?
- How to Cope Up with a Bad Router?
- 1. Strategic Router Placement
- 2. Use an Ethernet Cable
- 3. Change the Wi-Fi Channel you’re using
- 4. Use a Wi-Fi Extender
- 5. Use Electrical Wiring
- 6. Password
- 7. Reduce the burden of Unused Devices
- 8. Restart your router
- 9. Contact Your ISP
- 10. Overcome Overheating
- 11. Check Your QoS Settings
- 12. Update Your Router’s Firmware
- List of Bad Routers You Should Avoid
- The Verdict
How to Identify a Bad Router? [2023 Edition]
Well, your router is the single most important hardware for a wireless connection. To enjoy seamless connectivity, you need to know about the signs and symptoms to identify a bad router. Let’s take a look at the factors:
1. Unencrypted Guest Access
Most modern-day wireless routers offer connectivity to several devices. This is known as guest access. In some modern-day devices, this feature is available by default.
However, if you have security concerns, then some routers also allow you to choose to not allow certain devices access to your network. For this action, you’ll need to disable the guest access setting on your equipment.
The guest access setting on your router allows you to create a separate access point for your guests to connect to the Wi-Fi without a password. On such devices, you can set up this feature by logging into your router’s admin panel.
Basically, by setting up a guest network you’re connecting several other devices to a secondary network and setting up a security blanket around your primary network.
Some routers botch guest mode, how? Well, when you enable a guest network, you’ll immediately be able to see that it’s like an open Wi-Fi network.
It means that your guest network is not as protected as your main wireless network via encryption. This further implies that any device seeking access to your guest network is given an all-clear and your network becomes vulnerable to snooping.
If you have a dual-band or tri-band router that operates using multiple frequency bands, then you may experience a poor wireless connection. Some devices even allow you to limit the time for which other devices can stay connected to your wireless connection. Sounds interesting, right?
The connection is not encrypted and is therefore prone to cyber-attacks. Modern-day operating systems warn you about the same too. But there’s a catch. After a device asks for the guest network access, the device is asked to put in a passphrase on the webpage. However, anyone spying on you while you’re putting in your password can gain access to the Wi-Fi guest network.
If your chosen router offers an unencrypted guest mode, then it’s probably not a good idea to invest in it. Moreover, with a permanently on guest access setting, you’ll have to change your password over and over again to avoid any security mishaps. That can certainly be irritating too, so make sure that the device you’re getting has an option to enable or disable the guest network.
2. Lack of Quality of Service (QoS)

When using a wireless connection, you might have tasks that require extra attention and better Wi-Fi speed. For this purpose, you need to have an optimum bandwidth in order to perform them.
However, your Wi-Fi network also witnesses packet requests from other devices that use the same bandwidth. This can lead to your network becoming congested and your important data packets may have a hard time reaching their destination. This is where the Quality of Service or QoS of your router comes in.
It is a feature that enables your router to prioritize certain devices or types of traffic. It assigns high priority to critical traffic and a low priority to traffic that doesn’t need a high bandwidth at all times.
So, basically, the QoS allows you to tweak the traffic flow on your Local Area Network as well as the traffic flowing in and out from your ISP and WAN connections.
It is an essential feature for businesses as it allows you to prioritize certain services no matter how high your bandwidth usage is. In the same manner, several non-critical backup operations can be given a lower priority.
These operations can then be carried out by your router at night when your bandwidth usage is the lowest. Most modern-day devices allow you to enable the QoS feature in your home and business. When configured and enabled properly, you’ll notice that your critical network communications and traffic enjoy better speeds.
This leads to better working efficiency with no slowdowns. But if you have a traditional router at your home, then it can be a problem. A traditional router treats all network traffic equally and if you have a device that does not have QoS capability, then it will not recognize the instructions of the server.
3. Outdated Firmware
Outdated firmware can pose a lot of problems for both your business and home. But do you have any idea what firmware is? Every hardware has a basic type of software that is known as firmware. The firmware of your device is only compatible with the hardware that it came with and it cannot be uninstalled or replaced.
The firmware of your router allows your devices to update and modify settings so that other higher-level software can interact with it.
All the information on your device passes through your router. And if that is compromised, it can lead to a lot of security issues. But I’m sure that the most interaction is an occasional turn-on and turn-off. However, this kind of neglect from your side can put a lot of personal and important information at risk.
If the firmware of your router is outdated, a successful cyber-attack can give hackers access to a lot of your files. In fact, several hackers may also be able to record the websites you visit, the searches you make, and they can even re-route you to certain other websites. Hackers can even take over your router to conduct illegal downloads and attack other websites.
A study conducted by Tripwire claims that only 41% of the people update their router firmware regularly. And only 32% of them knew how to update it, This means that more than half the population has got no idea about firmware updates.
If you have static software running in your router, then there are chances that your wireless network will be highly insecure. As the firmware cannot be uninstalled or replaced, the only thing that you can do to replace it with a new router.
4. Bandwidth Throttling
When your Internet Service Provider intentionally speeds up or slows down your wireless network connectivity, it is known as bandwidth throttling. This measure is employed in communication as a reaction to network congestion in order to regulate network traffic. It can occur at different levels.
For LAN, a system administrator (person responsible for reliable operation of the computer software) may help limit network congestion and crashing servers.
It is sort of business for Internet Service Providers. If they slow down your internet speed, then they’ll charge you the same amount for data per month. For instance, if you are subscribed to 100 Mbps plan and only get 50 Mbps, then the speed shall reduce (take extra time to download) but would consume same data amounts right? This is generally noticeable in the Unlimited service packages.
Bandwidth throttling can have multiple effects on your daily life. For example, if your ISP is throttling your router speed, then your speed of uploading and downloading during video streaming or using BitTorrent or other using other file sharing applications may slow down.
Furthermore, your ISP can also tweak the bandwidth available to all users across the network. This technique is also used by your ISP to reduce the local area network connection by spreading the load over a wide network or a number of servers to avoid overloading individual ones.
This helps reduce system crashes and it provides your ISP an opportunity to convince you to invest in more expensive pricing schemes in order to enjoy better bandwidth. Another reason why they might be throttling your internet is because of data capping.
You must’ve noticed that your internet becomes slow towards the end of the month. This is because your ISP controls how much high-speed internet you can consume on the basis of your billing cycle.
One way to bypass bandwidth throttling is by using a VPN. Most modern-day routers support it but the traditional ones don’t. Additionally, a lot of devices support VPN only as a server.
Many devices with built-in VPN servers enable you to connect to your home network while you’re away but they can’t act as a client. This means that they provide zero support for bridging the router to a remote VPN.
5. Interference Issues
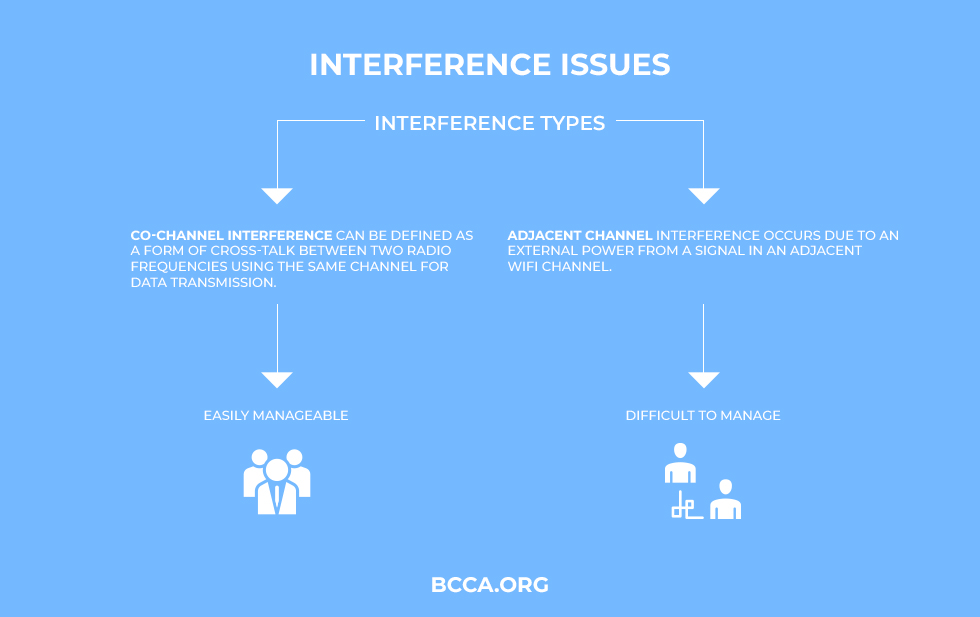
Interference can be of two types; co-channel interference and adjacent channel interference. The cochannel interference can be defined as a form of cross-talk between two radio frequencies using the same channel for data transmission.
So, in co-channel interference, your devices have to wait in line to talk with your access point. However, wireless conversations remain managed.
Adjacent channel interference occurs due to an external power from a signal in an adjacent Wi-Fi channel. There can be multiple reasons behind it. Some of the reasons are incomplete filtering of radio waves, poor frequency control, or improper tuning.
The reason why you should care about co-channel and adjacent channel interference is that it can severely affect your data transmission speed. While adjacent channel interference can be difficult to manage, the co-channel interference is fairly easily manageable. The only solution to it is to use a 5 GHz frequency band.
It is because the 2.4 GHz band is not just compatible with your laptops, tablets, or PCs, but also works with household devices such as microwaves, cordless phones, etc. It can lead to a lot of network congestion because all your household devices will be competing for the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
This particular problem is especially prevalent in single-band routers. They only employ the 2.4 GHz frequency band for data transmission. Therefore, if you have a single-band router at home, then you’ve got to blame this band for slow speed.
The only solution to this problem is to replace your single-band router with a dual-band/tri-band. The latter employ both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. So, if you want better speeds, then you’ve got to bid goodbye to your single-band router.
6. Overheating
The most common reason for wireless routers going bad is overheating. These are the devices that provide us a wireless connection to your homes, schools, business, etc. However, they can go bad over time due to overuse. It is because most of us leave them on for 24 hours resulting in overheating.
Overheated routers result in dropping internet connections for varying amounts of time. Sometimes these dropped connections can last over several hours. Another problem encountered is computer screens freeze and snail-like connection speeds.
If your device is overheated then you’ll notice a flickering red light instead of a green/blue. This can serve as a diagnostic tool for such problems.
The worst-case scenario for that a scorching router can lead to is a complete hardware failure and can damage your computer’s motherboard too. In fact, if you touch it you can burn yourself and it can even lead to a fire at your place. Overall, the best indicator of a failing router is a failing wireless connectivity.
If that’s the case then your ISP might come to check if there’s anything wrong with their equipment. Just like other equipment at your home, your router also has a lifespan. They can last for a maximum of 5 years after which they’ll need to be replaced.
If you have a cheap router at home then you might need to replace it earlier than you thought. So, buying a cheap one might seem easy in your pocket at first but it can lead to a lot of problems in the long run.
7. High CPU Usage
Today routers process a large amount of data by the minute. And as you all know, the larger the network, the larger the amount of data packets flowing through it. You can experience serious network issues if your devices are suffering from high CPU usage.
If you’ve recently bought one with the latest hardware, then chances are that your device might come with a modern CPU architecture and could handle good amount of load. However, if your device has an outdated processor, then the usage shall be very high, thereby leading to throttling and overheating.
If you want to configure a lot of ACL’s on your device, but it can’t handle it, then it can lead to processing overhead in routers. This is especially problematic if your ACL’s are configured with multiple lists of modifying complexities.
You might be tempted to use data compression in order to boost your wireless connection speed, but think again. It takes a lot out of your router’s CPU. It can lead to overload and cause network latency.
Moreover, if you try to compress additional data on an already pre-compressed data packet the performance of your router can go down if it’s not equipped with a robust enough CPU to handle it.
A maxed-out CPU can also be a sign of adware or virus invasion. It can be a sign of a serious security breach. That’s why it’s recommended that you always invest in a router with a power-packed CPU to ensure that you don’t encounter the problems of maximum CPU usage and your personal information stays safe & secure.
8. Slow RAM and CPU
Your instincts may tell you to call your Internet Service Provider whenever you start noticing any hiccups in your wireless connection. This is because as the world becomes more technologically advanced, so do your needs.
Therefore, today you are required to connect more devices to your primary wireless network. And if your home or office has a router that can’t keep up with the ever-changing technology trends, then you’ve got yourself a problem.
You might be under the impression that a brand new router guarantees no internet hiccups but that’s not the case. Most of them are designed to handle the only basic network traffic and that’s why most of them fall on the cheaper side. You may not want to spend a lot on it but that can turn out to be a mistake.
After all, your router is the single most important piece of hardware in your wireless connection. That’s why it’s ideal to spend on a hi-tech device that offers you better CPU and RAM.
Such routers can handle more traffic with ease. It may have a modern CPU chipset but if it has a slow RAM, then you’ll experience several connectivity issues. If the RAM is less than 32MB, then it’s time to upgrade to a better one.
A router with a fast RAM can handle more data going back and forth easily. The problem with slow RAM is that if you over-utilize it, it can lead to a bottleneck effect.
And when you experience a bottleneck effect, your internet speed is bound to slow down. It’s just like being stuck on a highway with a lot of traffic and even when you feel like you’re moving, you don’t end up reaching your destination.
All your data packets need to go through your router and modem for processing. And it’s CPU and RAM play a major role in this processing. So, keep in mind that if you’re encountering buffering on a daily basis, it may be due to your outdated hardware.
Also, remember that this problem can occur with both cheap and expensive routers so you need to notice router specifications while buying one.
9. Bufferbloat
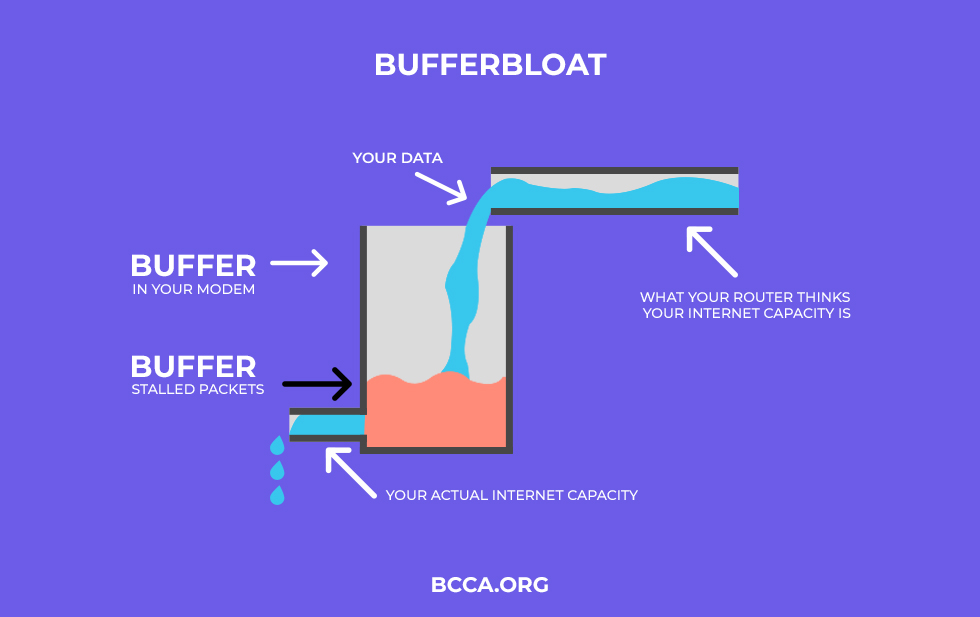
Bufferbloat is the latency or lag in data packet delivery by routers due to the buffering of data packets. It can lead to an overall decrease in the throughput and also lead to packet delay variation. Packet delay variation is defined as the delay in the flow of data packets without ignoring the lost data packets.
Sometimes this phenomenon is also known as jitter. When you expect your device to handle large buffers due to online gaming, web surfing, and voice over IP, you can experience network issues even if you have a high-speed Wi-Fi router. Some manufacturers unnecessarily design them with large buffers.
In such routers, when a Wi-Fi channel becomes congested, the bufferbloat phenomenon occurs, leading to data packets being left in the queue for a long time.
Large buffers result in long data packet queues resulting in poor network throughput. To figure out whether or not it has buffer float, you can use the Speed Test. If the test shows a lower grade than B, it means that you probably have bufferbloat. This means that your router is allowing large traffic to interfere with your time-sensitive network traffic.
That’s why it’s important to buy a wireless router from a manufacturer that understands what bufferbloat is and installs a Smart Queue Management Algorithm such as cake, PiE, fq_codel, etc. in it. You can manage your SQM settings to put a halt to any bottleneck effects in it. If there is no SQM feature, then consider replacing it.
How to Avoid Buying a Bad Router?
Today, no one can imagine living without wireless routers. So take a look at the following factors to look to buy the best functional router for your needs:
1. Move Along the Digital Trends
As technology becomes more advanced, router manufacturers are implementing the new wireless standard to compliment your latest devices. Wireless standards such as 802.11b, 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11AX (Wi-Fi 6), etc. describe the capabilities of your device. If it doesn’t keep up with the latest trends, then it may become obsolete in the long run even before the end of its lifespan.
2. Wi-Fi Network Speeds
Always remember that the practical speed that your wireless router offer won’t be the same as the theoretical number. Having said that, some cheap devices offer a wireless speed of 100Mbps which won’t be sufficient even for your everyday tasks. That’s why it’s best to go for wireless routers with a theoretical speed greater than 300Mbps.
3. Decide the type of router
Technically speaking, there are 3 kinds of routers that you can opt for. The first kind is a single-band device that operates on a single 2.4 GHz frequency band. It’s sufficient for home use but you’ll struggle with it if you use your wireless network for high-end tasks such as business workflow and online gaming.
The second kind is the dual-band router that uses both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. Although this one offers you higher speed, it lets you down in the range department. And the latest and the greatest kind is the tri-band router which operates on one 2.4 GHz frequency band and two 5 GHz frequency bands. It’s perfect for gaming and business purposes.
So, choose your Wi-Fi router according to your daily requirements.
4. Wi-Fi Security
Wireless networks aren’t as secure as they’re convenient. If you don’t pay attention to your router’s security configurations then any hacker can gain access to your personal information stored on various devices. Therefore, it is essential to make sure that any you buy supports at least WPA2 Wi-Fi protection protocol.
In fact, today many modern-day routers support even WPA 3 with enhanced wireless security features. Also, bear in mind that some of them are designed with keeping advanced security features in mind. Therefore, these devices come with extra features such as extra encryption, the ability to block unwanted devices, etc.
5. Wireless Management
Honestly speaking, your wireless network is of no use to you if you encounter frequent co-channel and adjacent channel interference. This problem is mainly seen when using the 2.4 GHz frequency band. This is because the 2.4 GHz frequency band is used not just by your computer, laptop, or tablet but also by your other household devices.
Therefore, to overcome the problem of frequent wireless interference, you must choose the dual-band or tri-band Wi-Fi routers that operate on both; the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
Another solution can be to use smart devices that help you locate Wi-Fi dead zones. You can also buy several routers and place them strategically in your home to combat the issue of interference.
6. MU-MIMO Over SU-MIMO
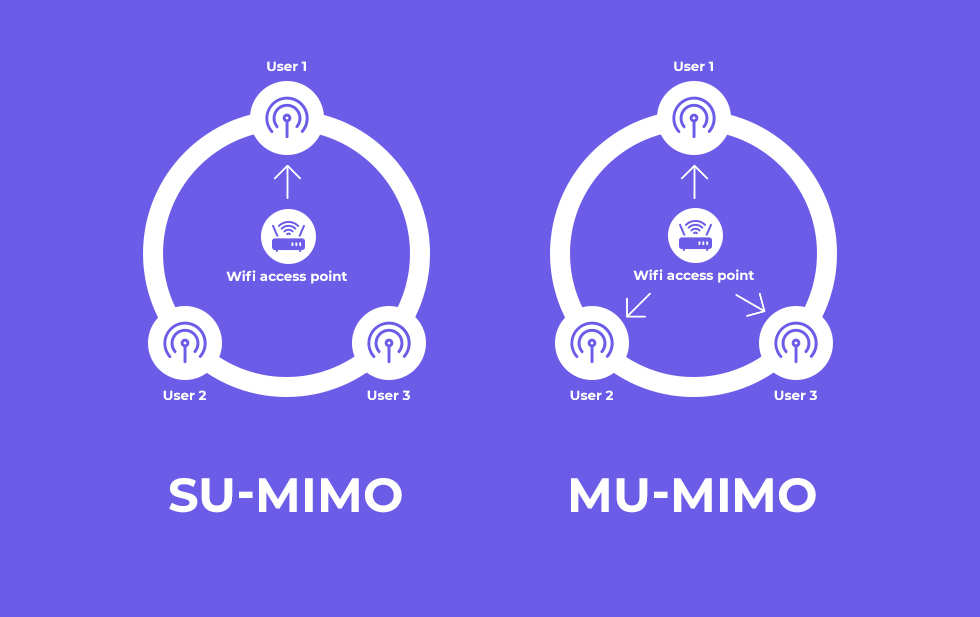
MU-MIMO is a significant technological development over the previously used SU-MIMO technology. It stands for Multi-User Multiple Input and Multiple Output. It allows several wireless devices to connect to your router at the same time.
This way your router can maintain a direct connection with several devices instead of shuffling data packets back and forth between one device at a time. It increases the throughput of your wireless connection and improves the reliability of your device.
In fact, MU-MIMO is all set to become a dominant technology in the future especially since it’s inclusion with the latest wireless standard, Wi-Fi 6 or 802.11ax.
7. Budget
I recommend that you at least set aside $100 to buy a wireless router that caters to all your needs. The problem with cheap routers is their slow CPU and RAM. Expensive models fall in the range of $250-$500.
But you don’t necessarily need to splurge such a huge amount of money if you don’t require a router with extensive abilities. It’s always best to buy a hardware piece that performs daily tasks with perfection and is easy on your pocket at the same time.
How to Cope Up with a Bad Router?
If you’re in a catch-22 sort of situation and don’t have the money to buy a better router, then don’t worry. I’ve got a few tips that you can use to upgrade your Wi-Fi without purchasing a brand new device. Take a look:
1. Strategic Router Placement
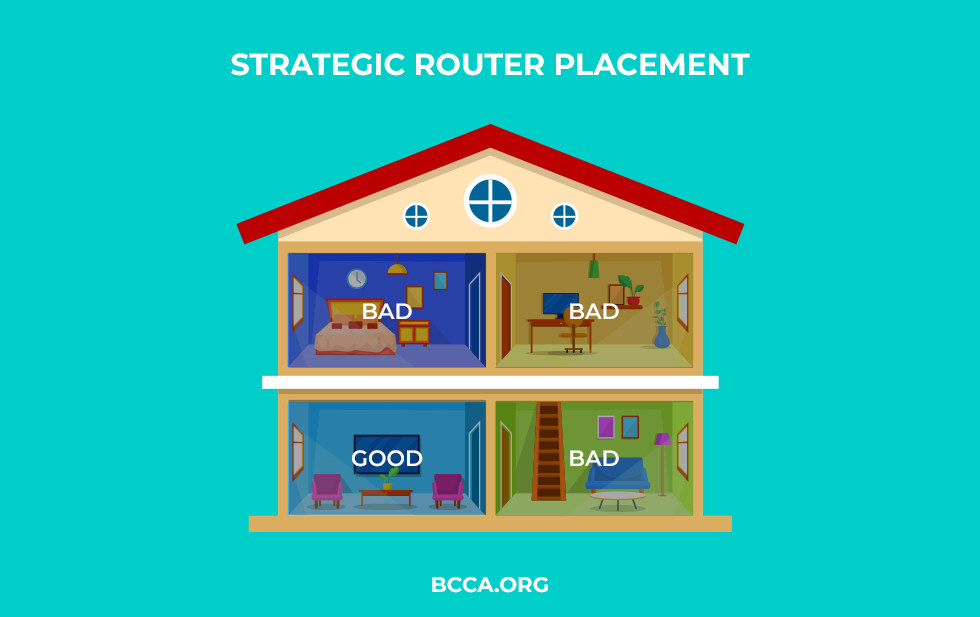
The position of your router plays a great role in determining the speed of your wireless connection. If it is placed in an area with a lot of furniture around, then it won’t provide you with the speed you desire. Physically moving it can make a huge difference in the range of your wireless network.
You shouldn’t hide it in a corner or inside a cupboard, but place it in a more central and prominent area with a flat surface. Also, avoid keeping it near metal surfaces.
You might need to think about where to place your router but I promise it’s going to be worth the effort and with proper placement there’ll be less dead spots.
2. Use an Ethernet Cable
When you’re working on your computer, then it’s best to use the ethernet cable in order to enjoy a stable wired connection. An-d trust me, you’ll thank your lucky stars for it. The only downside to a word connection is the number of devices you can connect with. But if you want to manage the number of wires being used, you can keep the ethernet cable fixed to the walls for better wire management.
3. Change the Wi-Fi Channel you’re using
The frequency band of your wireless network can be divided into several Wi-Fi channels. These channels are responsible for the transmission of data packets of information.
Certain Wi-Fi channels called overlapping channels are more prone to interference than the non-overlapping channels. So if you are facing a slow internet connection, it’s best to switch your Wi-Fi channel to a non-overlapping one.
4. Use a Wi-Fi Extender
If you have a few dollars to spare and you find it too daunting to play with your router’s setting, then I recommend you to invest in a Wi-Fi extender or repeater. These devices further extend your wireless network by focusing it in a particular direction using the method of beamforming.
5. Use Electrical Wiring
If you require a better wireless connection in a particular room, then you can use a powerline plug to connect to your router and then put the plugin a wall socket. This is a simple and effective option to boost your Wi-Fi connection.
6. Password
If your router doesn’t provide a good security option, then I highly recommend you to change your Wi-Fi password as much as possible. This will help you stay away from cyber-attacks until you’re able to invest in the one with better security options. Also, see if you can use AES encryption for your Wi-Fi password.
7. Reduce the burden of Unused Devices
Multiple devices can lead to network congestion if your router can’t support them. So my advice would be to use an ethernet cable for the devices you’re currently using and unplug the devices that you aren’t. It’s an easy way to make sure that you can perform all your tasks seamlessly.
8. Restart your router
Restarting or rebooting your router on a regular basis can fix your dead internet problems. This is especially useful if you’re using the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Rebooting it will enable the data packets to choose non-overlapping Wi-Fi channels leading to a faster internet connection.
9. Contact Your ISP
If you’ve tried all the above tips and are still facing the issue of bad wireless network, then I highly recommend you call your Internet Service Provider. Your ISP will send a service technician that will check if there’s any fault in your router hardware.
10. Overcome Overheating
Router overheating is a common problem that you must’ve encountered at least once. But it has a simple solution. Want to know what that is? You just have to switch it off when it’s not in use. Simple isn’t it? Also, make sure that there is enough room for air to circulate around it.
11. Check Your QoS Settings
The Quality of Service settings in a router controls the network traffic on it on a priority basis. If it has QoS configuration then make sure you enable this configuration in order to enjoy better Wi-Fi connection while performing your priority tasks.
12. Update Your Router’s Firmware
At times it can be attacked by malicious viruses and bugs that can bog down your internet speed. Therefore, it’s my recommendation that you always check your router for any firmware updates to enjoy a more secure wireless network.
List of Bad Routers You Should Avoid
I’m sure that you must’ve heard a lot about the best wireless routers in the world, but what about the ones that aren’t worth your time and money? Take a look at the following routers to avoid buying them in the future:
- NETGEAR RAX80
- To Link’s Archer C5400
- AirPort Extreme
- Amped Wireless Titan
- Securifi Almond+
The Verdict
If you think that your wireless connection is slow, then there can be several reasons behind it. One such reason can be a bad router. The technological advancements in the world of wireless standards help your evolving need of connecting multiple devices to the network at the same time.
But if it doesn’t work well, then your whole wireless data connection experience goes down the drain. Today you require a stable connection for more devices than you can count on 2 hands. Therefore, you need a consummate Wi-Fi router to cater to all your needs.
You also need a stable wireless network now more than ever to complement your working from home lifestyle. I hope that this article answered all your questions regarding the problems you might face with a bad device and cope with it.
However, if you do have some dollars set aside then I’d highly recommend you to bid goodbye to your old incompetent router and say hello budget-friendly new device to enhance your user experience.
Chris loves technology, specifically smart home technology! With both hands-on and executive leadership experience in his corporate career, Chris stays abreast of emerging technology and solutions and immerses himself in BCCA when not in the office.
