A Wi-Fi Extender doesn’t directly slow down or speed up your internet. It only transmits the signals to the devices in an area where it wasn’t available before. The internet speed is mainly dependent on your router capacity. That said, there are other factors pertaining to Extenders that may affect your internet performance.
It relies solely on the wireless channels to communicate to the router and the other devices can practically affect your internet speeds. For instance, if the extender uses the same band for transmitting signals between the router, back and forth, it will create a time delay in communication. Thus leading to slower internet speeds.
Table of Contents
Does Wi-Fi Extender Slows Down Internet?
A Wi-Fi extender by default doesn’t slow down the internet connection, however, since it uses wireless mode of communication, it is vulnerable to various interferences that can hamper the internet performance.
The reason for a slower internet while using Wi-Fi extenders is multi-folded, with various factors playing their part, leading to slower internet speeds. Let’s take a look at the factors and how they contribute to slowing down your internet.
Physical Interference
Placing Wi-Fi Extenders near physical objects like TV or other gadgets or the under furniture can affect their performance. A household with multiple floors or several rooms separated by multiple walls isn’t an ideal environment for it to operate.
They can neither be farther away from your router nor the connecting device beyond too many walls. It further depreciates the internet speeds available to the devices.
Radio Interference

Wi-Fi signals are easily susceptible to external interference. A host of devices operate on a similar frequency to Wi-Fi devices. Devices like microwave ovens, baby monitoring devices, garage door controllers, Cordless phones, and Bluetooth devices.
When you extend your Wi-Fi signals, it leads to interference from nearby Wi-Fi networks. With interference and a higher signal-to-noise ratio, causes a delay between the communicating devices, further leading to reduced internet speeds.
Devices like video cameras, power lines, satellite communication transmitters are also less popular sources of interference.
Wi-Fi Extenders connect to an existing network and broadcasts a network with a new name. Any device accessing a network stays on it until it goes out of range completely.
You will find intersectional points at your home where both the networks are available but at different signal strengths. Either the signal from the router can be strong or from the extender.
The device connected to a weaker network might stay connected to the network until someone disconnects it manually. It creates a necessity to monitor the strength of the signals frequently. It might force the user to remain aware, and perennially switch back & forth between two or more networks.
It might be a hassle to stay alert all the time. It will not be long before it leads to lower internet speeds, despite being in the vicinity of a stronger connection.
The Problem Of Half-Duplex Channels
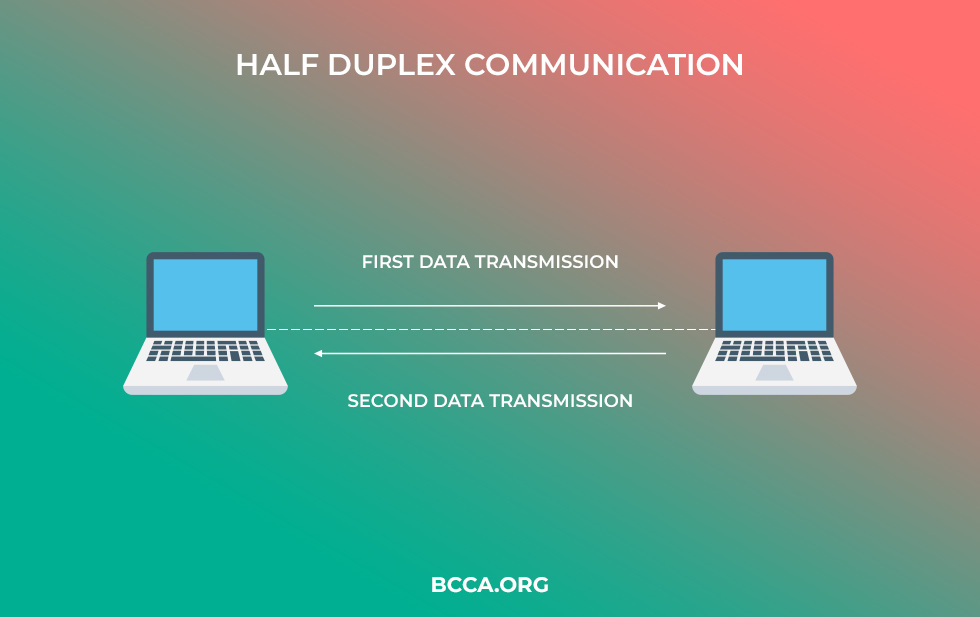
The wireless connections are half-duplex. Although the device can communicate in both directions, it cannot transmit and receive at the same time. The extender communicates back and forth between devices and routers, resulting in loss of efficiency and internet throughput.
For every hop between the source and the destination, the internet throughput through wireless communication channels can reduce by 50%.
How To Fix Slow Speed Issues when connected to Wi-Fi Extender?
Multiple factors affect the quality of your internet speed. Addressing every single issue can go a long way in improving the speed of the internet.
Reduce Material Interference
There are multiple ways to improve the speed of your internet. First and foremost your extender should never be placed behind any physical object. It degrades the signal quality right away. If you can set your device at a higher elevation, it would help in minimizing any further material interference.
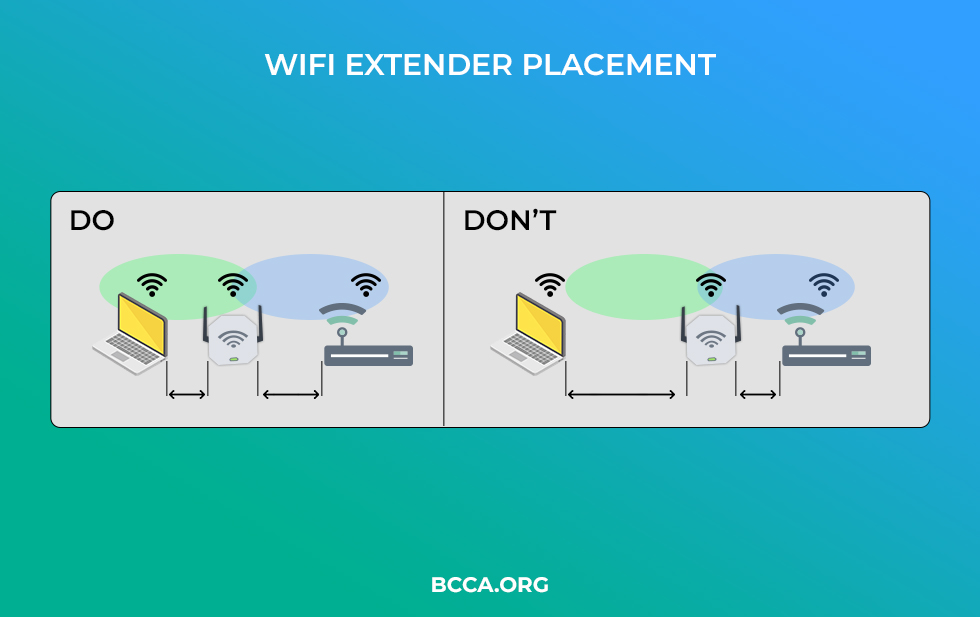
Placement
The Extender placement is imperative to the signal strength. Placing your Wi-Fi extender at a central location can substantially improve the quality of the signal, leading to an increase in speed.
Furthermore, it should be placed at a location where it receives a stronger signal from the router. Moving the device farther away from the router leaves a weaker signal. The extender ends up transmitting weakened signals to the devices.
The placement of the extender remains a crucial factor that affects your internet speed.
Connect via Ethernet Cable
Use an ethernet cable to connect your Wi-Fi extender to the devices and the router as much as possible. It reduces the substantial loss of bandwidth and delivers an improved internet throughput, not exceeding the internet speeds from your ISP.
If your extender doesn’t have multiple ethernet ports, use an ethernet hub to connect your TV/gaming console/Work desktop. It ensures the highest bandwidth is available for your priority devices.
Use Dual-Band / Tri-Band Extenders
The Wi-Fi extenders use the same radio band to communicate with the router and the devices. If you use a single band extender, the router extender spends half the communicating to the devices and the rest relaying the information to the router.
This effectively halves the capacity. To circumvent this situation, you can choose a dual-band or a tri-band extender. The extenders allow you to configure and allocate a dedicated band to communicate with the router and utilize the other available band/bands to carry signals to the devices.
Matching Wi-Fi Speeds
To get the best out of your internet, find an extender with a Wi-Fi speed that matches the Wi-Fi speeds of your router. You don’t want to lose internet speed because you never paid attention to the numbers.
External Antennas
Choose a Wi-Fi extender with external antennas. Antennas can play a vital role in transmitting Wi-Fi signals. Having adjustable external antennas gives you an edge in comparison to the extenders with just the internal antennas.
MU-MIMO
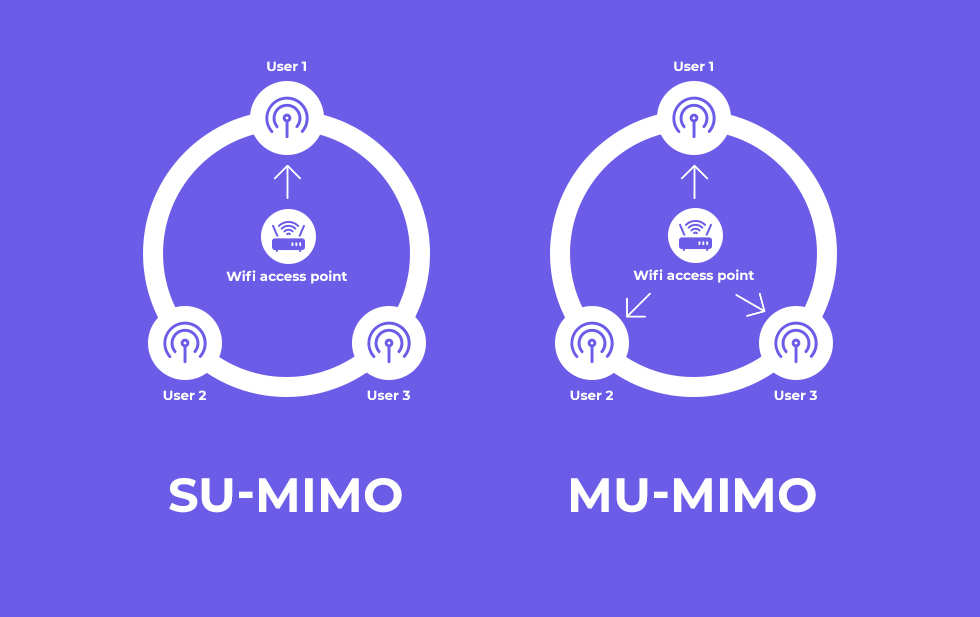
Look for an extender that is capable of sending data to multiple clients simultaneously. If the router supports MultiUser-MIMO and if you wish to extend the capacity to your booster, and handle multiple devices concurrently. An extender that supports MU-MIMO ensures the devices get faster internet speeds.
Efficient Alternative to Wi-Fi Extenders
Wi-Fi Extenders are not the only solution to avoid dead spots and improve internet speeds. Basic extenders can improve your range without having to upgrade your internet connection, at a low cost. But their application is limited and is not effective in larger homes with multiple floors.
Here I discuss 2 Wi-Fi Extender alternatives that you can consider in case you’re experiencing major speed or coverage issues:
1. Wi-Fi Mesh Network
Mesh Wi-Fi systems offer a better alternative if you are looking at getting high-speed internet for multiple data-intensive devices with a consideration of future-proofing your system for higher internet speeds.
If you are looking forward to upgrading your network, mesh-based Wi-Fi systems offer an alternative to covering large homes. The mesh systems have a primary router and multiple satellites/nodes that can be placed at different points at your home.
They share a single SSID and offer seamless roaming throughout your home, without the need to manually switch between networks. Mesh systems operate either on dual or tri-band, and that minimizes the chances of congestion.
With support to band-steering and MU-MIMO, the mesh systems can automatically route your device to the best available band and concentrate signals towards your device. While they come at a price premium, it can be a worthy consideration, after you evaluate personal preferences and requirements.
Wi-Fi Mesh systems also offer a user-friendly uncomplicated interface and advanced security options to manage your home network.
2. Wi-Fi Repeater
Most of the networking brands interchangeably use both terminologies while referring to any of the Wi-Fi signal boosters (i.e. Wi-Fi Extender/Wi-Fi repeater). The purpose of these devices remains the same. To capture the signal and re-transmit it to devices in an area beyond the range of the router.
The previous generation of Wi-Fi boosters was predominantly called Wi-Fi repeaters. The recent Wi-Fi boosting devices go by the name of Wi-Fi Extenders/Wi-Fi Range Extenders. The Wi-Fi repeaters are connected to the router wirelessly, like any other device connecting to the router, say a mobile phone or a laptop.
Conclusion
A Wi-Fi extender has its advantages and disadvantages. It offers a budget-friendly solution to extend the coverage of your router. While it can be a feasible alternative for medium homes with limited devices, it starts becoming less than ideal as the size and the number of devices increase.
As the features improve to cater to advanced requirements, the cost surges upwards. The recent rise of Mesh Wi-Fi systems with support to the latest wireless standards and advanced band steering makes them worthy of attention.
Chris loves technology, specifically smart home technology! With both hands-on and executive leadership experience in his corporate career, Chris stays abreast of emerging technology and solutions and immerses himself in BCCA when not in the office.
