Are you staring hard at the networking shelf of the local electronics store, without having any clue about which device to pick? Well, you aren’t alone as for a layman; the concept of connections is heavily clouded by his or her innate ineptness.
Modems and routers are two essential breeds of networking devices, apparently with different responsibilities. But then, most users are left bewildered when it comes to making separate selections. Once and for all, you need both a modem and router to access the internet, period!
But this statement wouldn’t make sense unless you compare and understand the basic differences, networking conformities, and the glaring contrasts that are embedded within the operational schema of each networking breed.
Table of Contents
Modem vs. Router: The Difference
Now that I have established that a modem and a router are two completely different networking devices, you shouldn’t lose sleep over learning the networking concepts that define the underlining technology.
Instead, I shall be keeping the discussion highly undemanding and immensely comprehensible. But then, let’s get the basics out of the way.
What is a Modem?
Let’s ditch the theoretical explanation for now. In simple words, a modem is a device that actually connects you to the internet. Confused?
I bet you must have thought that it’s a router that connects you to the internet. Although this fallacy doesn’t surprise me, it does require a pretty simple explanation to debunk, putting the modem in focus.
For starters, the modem converts the analog signal transmitted by the cable, fiber, phone lines, or any relevant form of wiring into digital bits of data that is understandable by the computer. A laptop or a PC doesn’t have a direct port to accommodate the coaxial cable or the optic fiber.
Instead, it needs to be first fed into a modem that modulates the signal into a more usable form. Also, a modem even demodulates the digital signal and sends forth analog signals through to the ISP, for the provider to monitor certain facets of the usage.
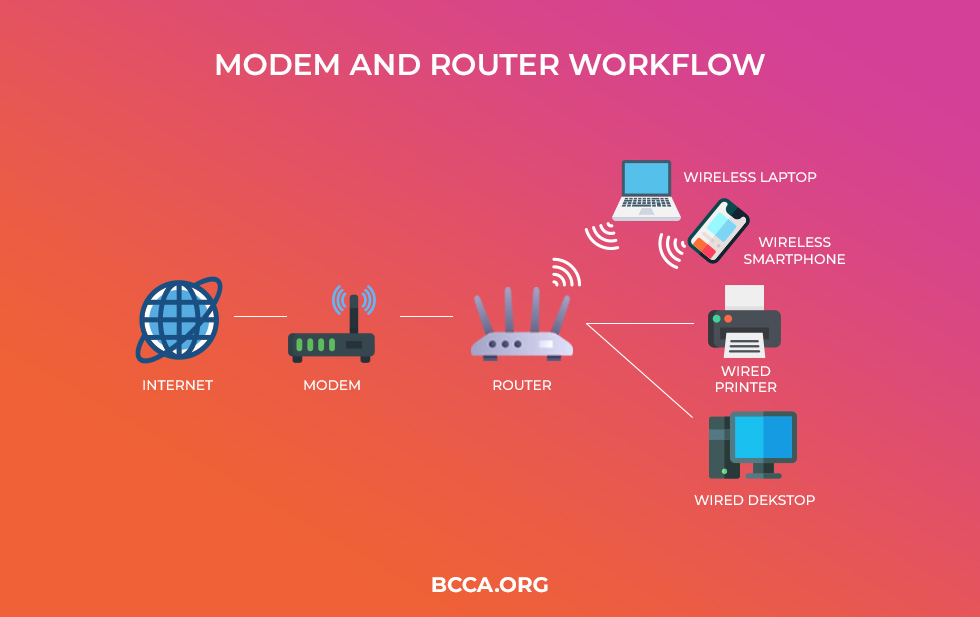
To sum it up, a modem is a device that connects the home network to the wider world of the internet.
Types of Modem
But then, every modem isn’t the same, and here are some of the variants that you need to look at before making the purchase, as per the type of wiring provided by the ISP:
- Cable Modem
Here is the most common form of modem that is capable of carrying and processing television and radio signals. A cable modem ensures that the signal relayed by the existing television line is converted into a compatible, digital mode, either internally or externally.
- DSL Modem
This device is meant for accommodating the twisted cable, which transmits data and signals at speeds reaching up to 2Mbps. The higher transmission frequency covers a wider area as compared to the dial-up devices.
- Dial-Up Modem
Probably the most dated modem variant, a dial-up device is hardly seen in modern-day households. The differentiating trait, however, has to be its ability to use the analog phone line for establishing connections, by specifically modulating the carrier signals.
- Mobile Modem
Better termed as a wireless modem, this device comes integrated with the laptop or a standard PC. However, one can even use them as wireless USB drives for being connected to the internet, even on the move.
- Duplex Modems
Unlike some of the other variants on the list, duplex modems can be segregated into half and full-duplex devices, with the former allowing one-directional transmission of the signal. Full-duplex modems can transmit data bi-directionally, in a concurrent way. Most high-end, modern-day modems are full-duplex.
- FOM
For connecting ISPs offering internet via fiber optics, you require a special kind of modem i.e. the FOM. A ‘Fiber Optic’ modem differs from standard DSL and cable counterparts as the signal is transmitted over fiber optics instead of copper cables.
What is Router?
A router, on the other hand, carries the decoding internet from the modem and transmits it as wireless or wired connections. When connected to the modem, the router creates a Wide Area Network, which is synonymous with internet access.
However, if there are multiple smart devices at home, a router can help establish connections between each, by creating a local area network or LAN.
If you want me to put this in a simpler manner, a router is basically meant for routing data, whilst creating a link between the internet and numerous devices.
Types of Routers
Depending on the coverage, technology, antennas, and add-on services, routers can be segregated as follows:
- Wireless Router
Any routing device with support for multiple access points can be termed as a wireless router. Also, it needs to have LAN switches to support wired connections.
- Modem Router
If you have multiple PCs to connect to the DSL transmission line, specifically for gaining high-speed Internet access, a modem router is your best bet. It also comes with NAT support for added security. You can also tag this as a gateway device for better clarity.
- Core Router
Any router that is placed at the center of an internet or intranet ecosystem is termed a core router.
- Edge Router
Mostly used in corporate setups, an edge router is all about transmitting data between two separate networks and not within any given network.
- Virtual Router
More of a software-specific function instead of a physical device, a virtual router is synonymous with the hotspots on PCs and Smartphones.
In addition to these segregations, you can also select between WiFi AC and WiFi AX routers or routers with external and internal antennas, depending on the usage.
Modem or/and Router: Which one to Buy?
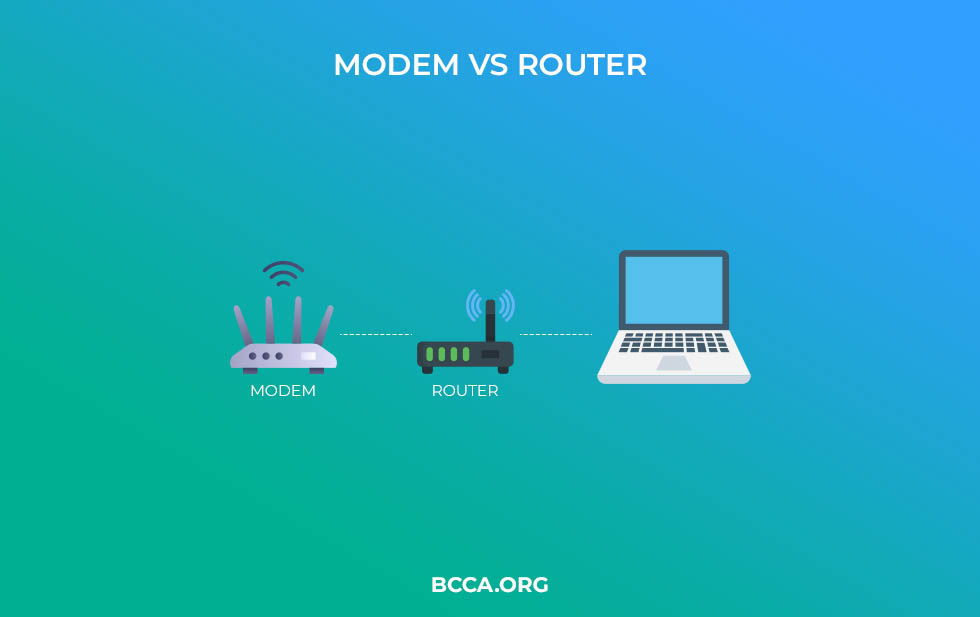
If you want to connect the home network to the wider internet whilst making bandwidth available wirelessly to smart gadgets, you would need to invest in both these networking devices. While the modem connects you to the internet, only a router can make it usable for smart devices.
Also, if you are getting speeds lower than that promised by the ISP, the router might very well be the reason as it is more prone to signal attenuation. However, you can fix this bottleneck by getting hold of a modem-router combo.
Modem and Router Combos Explained
Companies like Linksys, TP-link, and more offer combo devices with modem-like and routing capabilities integrated into one. As the hardware remains the same, signal loss experienced due to modem-router connections can be eliminated.
While the cost of one combo device is usually lower than the cumulative buying cost of the modem and router, you need to change the entire device if one aspect of the same stops working. Also, as the router is often the reason for slower internet, a combo might hinder your ability to upgrade the setup, in case you move to a larger house.
Frequently Asked Questions
If you still live under the rock and only have a PC to connect to the internet, a modem is more than adequate. However, if plan on connecting the smartphone or any other smart gadget to the internet, either wired or wireless, a router with decent coverage becomes important.
As these are two separate devices, it is imprudent to categorize them in terms of functionality However, if you still need to choose one, I would recommend going with the modem as it connects you to the internet in the first place and can connect at least one wired device to the internet if not all.
No, a router cannot fill in for a modem as it doesn’t have the hardware or technology to decode the analog ISP signal and directly connect to the wider internet.
If you are hunting for a modem, it is advisable to pick one depending on the ISP’s wiring, DOCSIS support, and the number of downstream and upstream channels. However, with routers you can be a bit more adventurous and look for coverage, far and near band speeds, MU-MIMO support, QoS, number of bands, support for VPN, the number of Ethernet ports, app access, and more.
Conclusion
To sum it up, both modems and routers are essential networking components with the former connecting you to the internet in the first place. The latter is responsible for routing the internet far and wide across the establishment, depending on its potential.
But then, you need to know that a router can create its own network for connecting other smart devices for interacting and transferring data between each, even without the internet connection. So, both the devices have separate functionalities and you must not confuse them for anything alike unless there is a combo to work with.
Chris loves technology, specifically smart home technology! With both hands-on and executive leadership experience in his corporate career, Chris stays abreast of emerging technology and solutions and immerses himself in BCCA when not in the office.